In this digital era, life without the internet is not possible at all. Countries across the globe have developed high-speed networks for keeping pace with technology. This is the century where technological advancement has gone through various phases. But if we talk of India, 5G in India is still a dream that is yet to come true in India. Why is 5G in India still a dream?

Problems in implementation of 5G in India
Here are some issues explained that are the problems in the implementation of 5G in India.
- India’s Telecom Sector: The telecom sector, although it has distributed broadband connections throughout the country, at the same time, it has also missed the even distribution of the broadband connection in India. Where the earlier 3G and 4G connections have not been adequately distributed in India, how can we even think of 5G?
- 5G needs a planned distribution structure. A proper strategy needs to be put to action for the implementation of 5G. But India’s regulatory bodies are lagging far behind, which makes it nearly impossible to implement 5G in India.
- Fiber infrastructure: For any new generation network to be implemented, fiber infrastructure plays an important role. But India is still lagging in this also. For the implementation of 5G in India, fiber infrastructure needs to be enriched. Fiber infrastructure aims to improve voice calling quality and deliver increased data capacity.
- But in India, this is a significant problem that hinders the speed of the internet and results in poor voice calling quality. The reason for poor fiber infrastructure is that India has not put much effort and investment into upgrading its fiber infrastructure. This results in insufficient data and networks in India.
- Low speed of data: India ranks 87 out of 147 countries in terms of average internet speed. The speed of data in India is below average that means India has a relatively low data speed. When it comes to rural areas primarily, many issues are related to the rate of the data. Issues, like downloading or uploading an HD video, game, or downloading, or uploading any large-sized file, are still problems in rural areas. This is because the data is not uniformly distributed throughout the country.
- High rates of the internet: India has a low data speed, but India’s rates are still very high. Various economic factors are the cause of these high rates of the internet in India. Despite these economic factors, corruption is also an important reason that cannot be missed out while computing the internet rates in India. Thus, India is lagging far behind in the ranking list of countries in terms of average internet speed.
- Last-mile connectivity: As discussed above, India is lagging in fiber infrastructure, which has affected last-mile connectivity. NOFN was a project that linked up all the gram panchayats in India. Nearly 2,50,000 gram panchayats of India were linked up in this project. The aim of this was to improve the quality of last-mile connectivity in the rural areas of India. This work was divided between 3 telecom companies, but it seemed that a few places were connected after two years.
For implementing 5G in India, uniform distribution of network is essential, which is what India is failing. Many things are to be followed for implementing 5G in India, and many connections are to be upgraded.
Solutions that have been proposed for 5G implementation
Every problem has a solution for it, and similar is the case with this issue. Although many problems are arising for the performance of 5G in India, there are still some solutions that the experts have come up with for this issue. Following these solutions, the dream of 5G implementation can be achieved in India. Here are some solutions that have been brought in for this issue:

Mobile Edge Computing (MEC)
MEC (Mobile Edge Computing) is a form of edge computing that expands cloud computing’s capabilities by taking it to the network’s edge. According to Cisco’s VNI Study, cellular networking and broadband technology evolution will lead to a 47 percent rise in global mobile data traffic from 2016 to 2021. When it comes to 5G, it will rely mainly on mobile network coverage and high data speeds.
MEC plays a part in dealing with these 5G features. The radio access network (RAN) has traditionally served as a “dumb pipe” for voice and data communications. By overlaying distributed edge cloud computing onto the RAN in the 5G network, operators would be able to make these pipes “intelligent.” Mobile network operators can enable multiple third-party tenants at the base station using virtualization at the RAN’s edge.
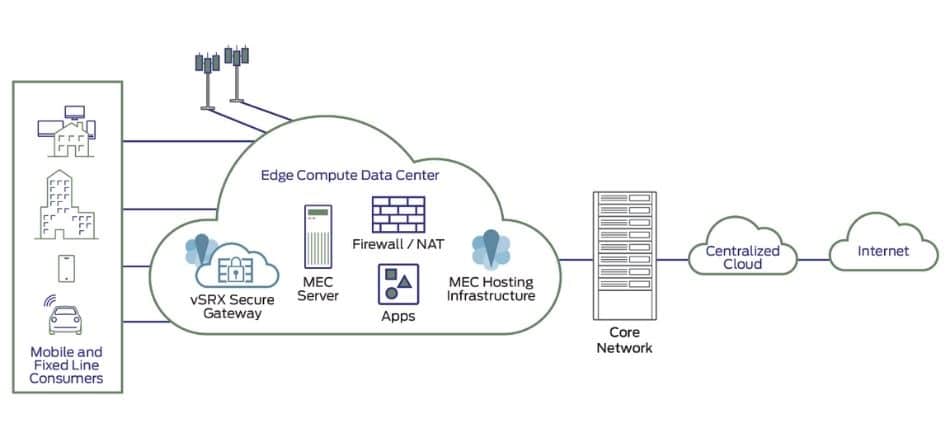
The following are the critical components of MEC architecture:
- Mobile edge platform: The mobile edge platform’s function is to define the configuration rules for the user plane traffic and compose radio network data in addition to the setup.
- Mobile edge orchestrator: Its job is to keep an overall view of MEC servers to determine the optimal positions.
- MEC application platform manager: This entity is in charge of the MEC application platform.
- Virtualized Infrastructure Manager: It handles virtualized infrastructure tools.
- Mobile edge applications: They function as a forum for other applications.
Software Defined Network
SDN (Software Defined Network) is built on the cloud computing paradigm and focuses on programmatically efficient network processes to increase the efficiency of existing network architecture. The primary goal of SDN is to unify traditional network systems into a single network. The control plane comprises two or more controller systems that carry out the entire centralization process.
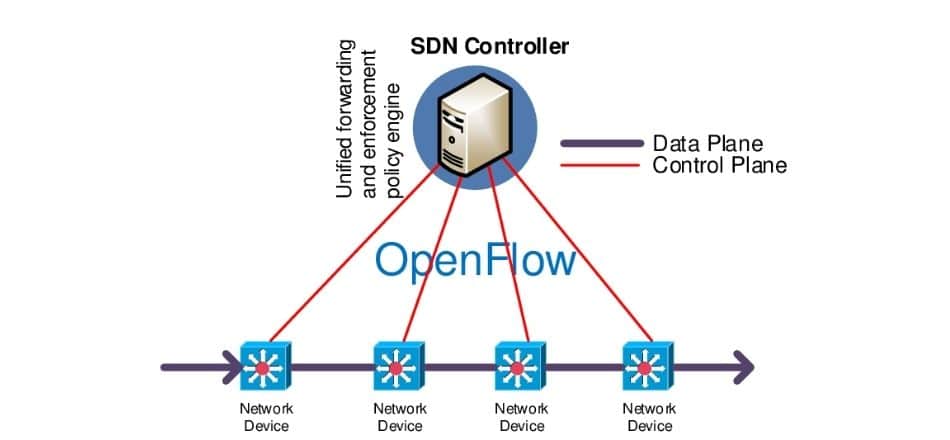
The network is divided into three layers:
- Application layer: This layer is responsible for communicating with the SDN controller via API (application programming interface).
- Control layer: The control plane(the brain) is housed within the control sheet. With the SDN framework’s support, which is present in the application layer, the SDN control plane prepares the logical map for efficient network decisions.
- The infrastructure layer: It is the final layer of SDN. It executes SDN data paths and forwards real traffic to the application and control layers.
How SDN aids 5G deployment?
5G prioritizes low latency, fast data rates, and low data traffic. SDN is critical to meeting all of these criteria. SDN would have a centralized network infrastructure for 5G, allowing for improved data flow bandwidth and latency reduction. Also, it will include a way to monitor network redundancy with the aid of a centralized control plane.
Deep Fibre
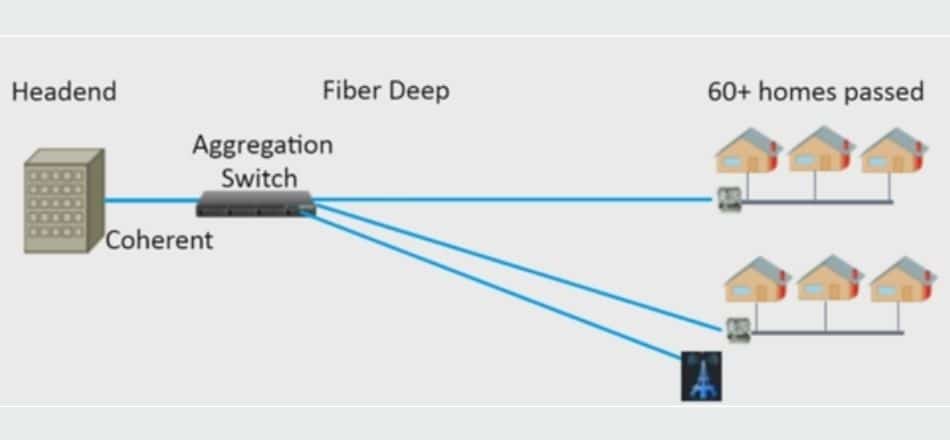
Fiber plays a critical role in the deployment of any network infrastructure. As previously mentioned in the segment on issues with the 5G rollout, India lacks fiber infrastructure and last-mile connectivity, and only 20% of towers have been upgraded for 5G technology. Deep fiber plays a vital role in solving last-mile access and fiber infrastructure concerns.
Deep fiber is a mechanism by which an MSO (multi-server operator) deploys fiber closer to consumers to provide better service. Deep fiber’s primary function is to eliminate amplifiers and bring optical-electrical conversion closer to consumers, resulting in increased bandwidth potential.
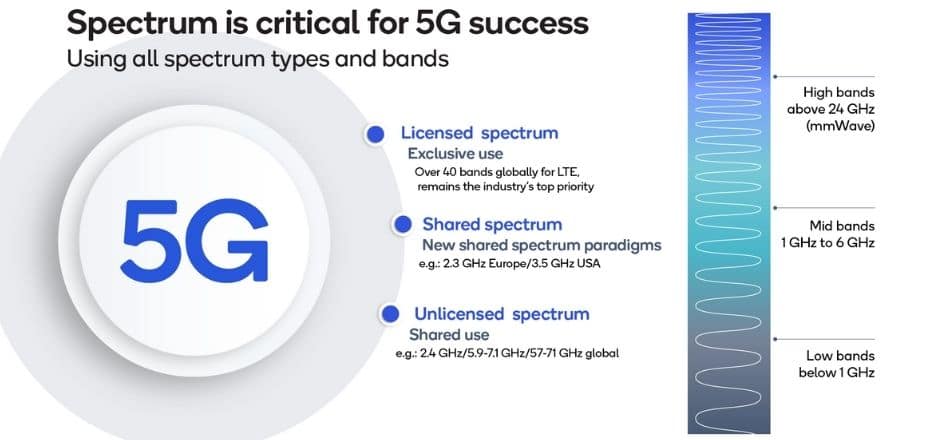
The value of spectrum in 5G?
Spectrum is usually distributed by auction in India. Regulators also consider the competitive nature of the downstream market when allocating bandwidth, designing auctions, and packaging lots. Spectrum limits are a tool for preventing spectrum concentration that harms the downstream demand. In harmonized 5G bands, sufficient, accessible, exclusively licensed, contiguous spectrum across the three leading frequency bands should be made available.
Spectrum policy initiatives that encourage 5G investment should be implemented. The Indian government and regulators will ensure the industry’s long-term viability and ability to finance the substantial investment needed for 5G network deployments by taking a long-term view, setting modest reserve rates, and prioritizing spectrum allocation.
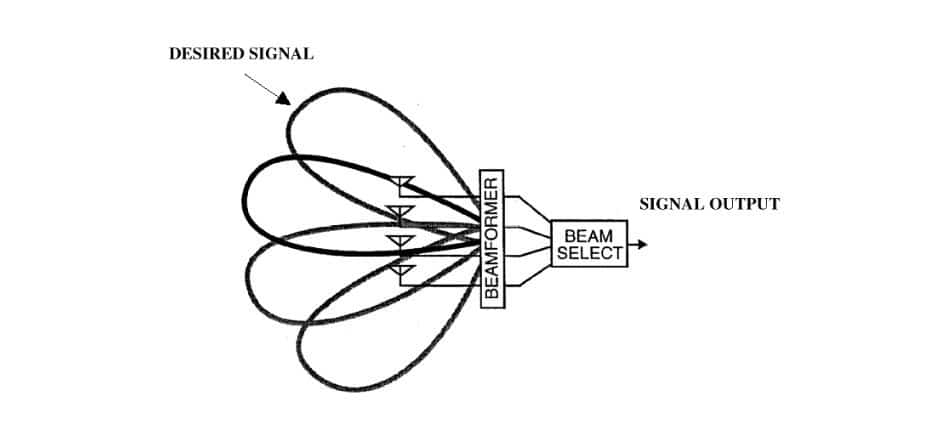
Smart antennas
Smart antennas are made up of multiple antenna arrays used to convert radio signals into narrow beams. The primary aim of using smart antennas is to enhance signal transmission focus through complex signal processing. Smart antennas are being used to help speed up the introduction of 5G. Since 5G would use a high data rate of 10 GB/s and a network capacity that is 10,000 times greater than the current network. To meet this target, the telecom company will need an additional broadband spectrum.
Smart antenna deployment can provide direct communications, reduce interference, and increase the ability to exist in cellular networks. Innovative antenna systems will play a critical role in assisting businesses in achieving this goal by growing network output capability beyond what is currently available.
With 5G implementation in India, our country will face a digital revolution. All the internet and data-based problems will finally come to an end with the upgraded 5G network in India. It will be helpful not only for the individuals but also for the commercial sector, defense, etc. This will lead to the overall development of the country. For similar development like other countries, the regulatory bodies of India need to look into the issues and get them solved as soon as possible.
FOLLOW US ON TWITTER, FACEBOOK, AND INSTAGRAM
Also, Read- What is edge computing? Is it the future of technology?
To learn more about Benchmarking, Click here.




